Starting in 2020, there is a new tax form for reporting non-employee compensation (NEC) payments to independent contractors. This form is called Form 1099-NEC. The IRS redesigned Form 1099-MISC for miscellaneous income. Payments related to NEC have been moved from Box 7 of Form 1099-MISC to Form 1099-NEC.
Small enterprise owners who hire independent contractors must use Form 1099-NEC to report payments. Form 1099-MISC, on the other hand, is used to report other miscellaneous income, like rent and prizes.
Let’s compare 1099 NEC vs 1099 MISC to determine which form your role must fill. We also suggest the key differences between these two forms and explain when they should be filed correctly.

What Is 1099-NEC?
If you’re a business owner or independent contractor, you may need to report payments of at least $600 per year for your non-employees. The IRS requires you to use Form 1099-NEC to report these payments.
You need to report payments made to non-employee individuals or businesses that didn’t file their federal income tax return as a C Corporation or S Corporation. This form also allows you to report any tax withheld on these payments.
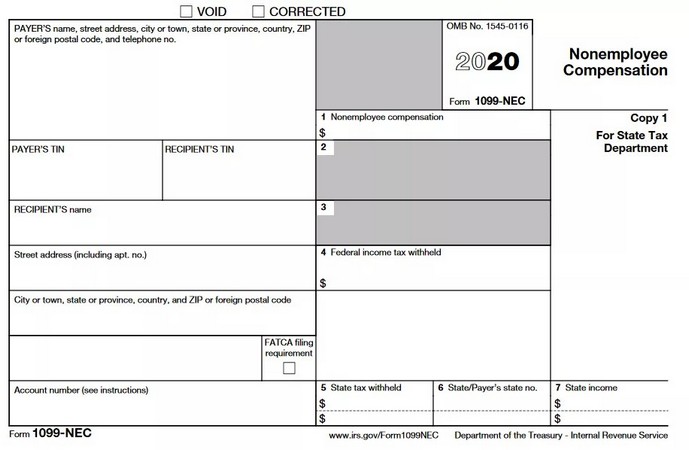
When you pay an individual, a partnership, an estate, or sometimes a corporation, you may need to report it on Form 1099-NEC. This form is also used to report payer direct sales of $5,000 or more in products to the recipient for resale, but you can use Form 1099-MISC for these payments instead.
While corporations are usually exempt from being reported on Form 1099-NEC, you must report attorneys’ fees (Box 1 in Form 1099-NEC) or gross earnings (Box 10 in Form 1099-MISC) of companies providing legal services on Form 1099. See the image below to navigate.
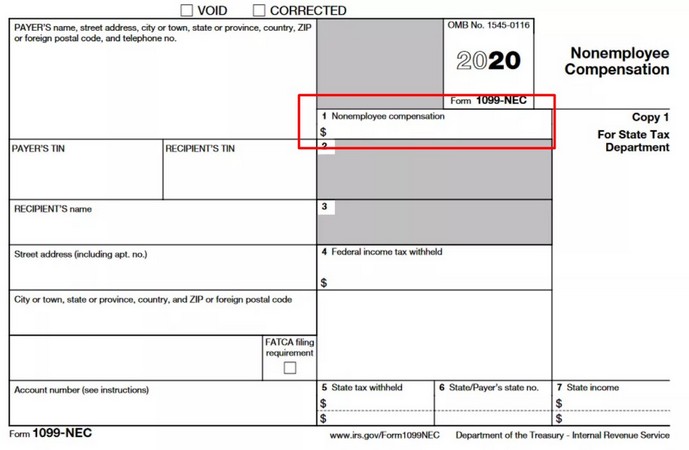
Independent contractors, whose payers report income on Form 1099-NEC, include freelancers or self-employed service providers operating as individuals or small enterprises (real estate agents not paid as employees, CPAs, tax professionals, attorneys, etc).
Employers must file 1099-MISCs by January 31 for any person or business that paid over $600 in deductible expenses during the previous year. Employers should also send the payee a copy of the 1099-MISC so they can use it to report relevant income when filing their taxes.
What Is Form 1099-MISC?
If you’re a business owner or freelancer who paid someone more than $600 for work during a calendar year, you’ll need to report the payment to the IRS using a form called 1099-MISC. This form is used to report specified miscellaneous income payments.
More specifically, employees should file Form 1099-MISC within:
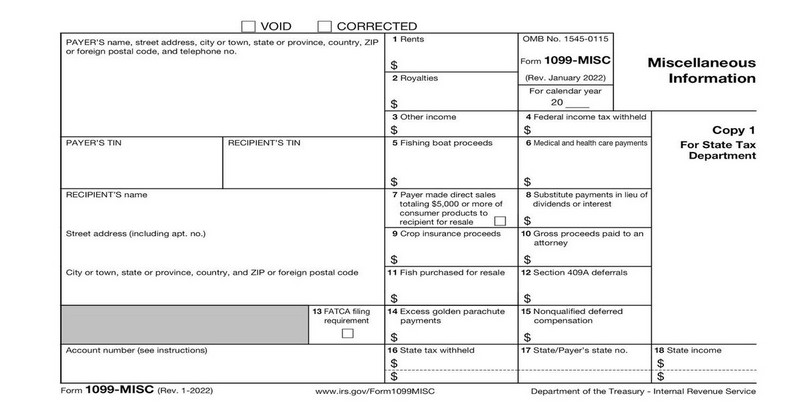
- Box 2: $10 or more in royalties
- Box 8: broker payments instead of dividends or tax-exempt interest
- $600 or more in:
- Box 3: Prizes, awards, income payments, and cash from ideational principal contract to an estate, partnership, or individual
- Box 5: Fishing boat proceeds
- Box 6: Medicare payments
- Box 9: Crop insurance proceeds
- Box 10: Payments to an attorney – claims gross income
- Box 12: Section 409A deferrals
- Box 15: Nonqualified deferred compensation
See the form below:
Form 1099-NEC is common in self-employment situations.
- Freelance work. Whether operating as LLCs or sole proprietors, writers, editors, designers, and other freelancers will obtain a 1099-NEC for compensation during a calendar year.
- Contract work. Any contractors not paid as W-2 employees through a staffing company (or otherwise have employment taxes withheld) will acquire Form 1099-NEC.
- Independent services. Any small enterprises doing legal or accounting work, network administration, web design, or services will file this report.
See more: Difference Between 1099 and W2: What Should Employers Know?
Key Differences Between 1099-NEC vs 1099-MISC
But ultimately, what is the difference between 1099 MISC and 1099 NEC? The answers including:
Nature Of Payment
Reports non-employee compensation of at least $600. This is income earned from providing services as a freelancer, independent contractor, or gig worker. The income reported on a 1099-NEC is typically subject to self-employment tax.

Reports various types of income of at least $600 that are not reported elsewhere. This amount includes rents, royalties, prizes and awards, fishing payments, and payments made to attorneys (excluding legal settlements). Income reported on a 1099-MISC may or may not be subject to self-employment tax.
Changes In Reporting Requirements With The Introduction Of 1099-NEC
Before 2020, you must report non-employee compensation on Form 1099-MISC. Starting in 2020, this non-employee pay is reported on Form 1099-NEC: Non-employee Compensation.
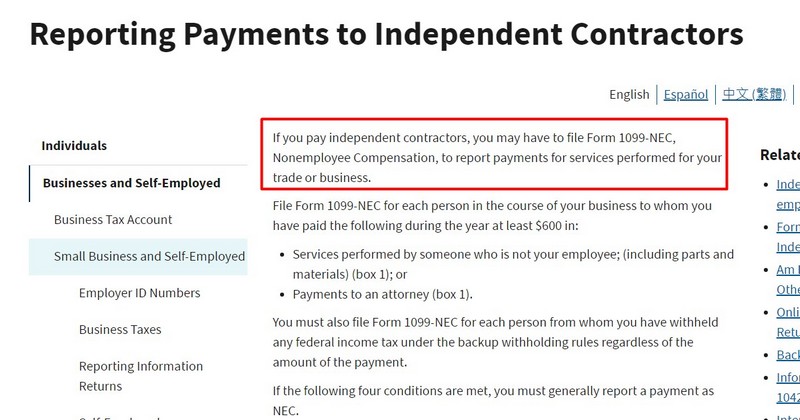
Image via IRS
The introduction of Form 1099-NEC streamlined the process by creating a separate form specifically for this type of income. This form aimed to improve reporting accuracy and tax collection for self-employment taxes.
Implications For Independent Contractors And Business
As a freelance or business, understand the difference between 1099 MISC and 1099 NEC. You must know the implication for each form:
- Freelancers / Independent Contractors:
- To understand the tax implications of your income, you’ll need to identify which form you receive (NEC or MISC).
- Income reported on a 1099-NEC will likely require you to pay self-employment tax (Social Security and Medicare).
- Businesses:
- Use Form 1099-NEC to report payments of $600 or more to freelancers and independent contractors for services rendered.
- For other types of payments not reported elsewhere on a 1099 form (rents, royalties, etc.), use Form 1099-MISC.
- File Form 1099-NEC by January 31 and Form 1099-MISC by March 31 (electronic filing) or February 28 (paper filing).
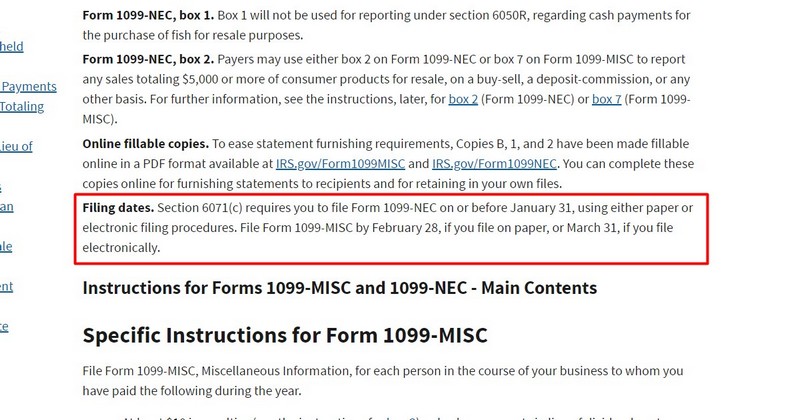
When To Use 1099-NEC vs. 1099-MISC?
Now you know what are the key differences between 1099 NEC vs 1099 MISC. However, choosing the right form depends on the nature of the payment and the recipient’s tax situation.
Determining factors for choosing between the two forms
- Nature of payment:
- 1099-NEC focuses on non-employee compensation, which means payments for services rendered by freelancers, independent contractors, or gig workers.
- 1099-MISC reports various types of income not reported elsewhere, such as rents, royalties, or payments to attorneys.
- Tax implications for recipient:
- 1099-NEC: Income reported is typically subject to self-employment tax.
- 1099-MISC: Tax implications vary depending on the income type. Some might be subject to self-employment tax, while others might not.
Scenarios Where One Form Is Preferred Over The Oher
- Use 1099-NEC when:
- You hire a freelance writer, web developer, consultant, or any other independent contractor for their services.
- You pay a musician, photographer, or other gig worker for their performance or work.
- The total payment for the year is $600 or more.
- Use 1099-MISC when:
- You pay rent to a tenant (if $600 or more annually).
- You pay royalties to an author or musician.
- You award a prize or honorarium (if $600 or more).
- You pay an attorney (excluding legal settlements, which are not reported on a 1099 form).
Ensuring Compliance With IRS Regulations:
- File Form 1099-NEC by January 31 of the following year (or February 28 for paper filing).
- File Form 1099-MISC by March 31 of the following year (electronic filing) or February 28 (paper filing).
- Provide a copy of the form (NEC or MISC) to the recipient by February 1 of the following year.
- Keep copies of all filed forms for your records.
Final Thoughts
Hopefully, after reading this article, you now understand the key differences between 1099 NEC and 1099 MISC. In short, 1099-NEC is for non-employee compensation, and 1099-MISC is for miscellaneous information and payments to non-employees. The IRS redesigned the 1099-MISC form when the 1099-NEC was created.
If you need to file either of these forms, knowing their meaning, usage, difference, and filing deadlines is important to business owners.
However, preparing these forms for international contractors can be confusing since they involve various legal liabilities in the United States. But you also submit the forms by the deadlines. Our solution, EOR Service, will help you overcome this situation. Contact ERA now!
Frequently Asked Questions
Is It OK to use 1099-MISC Instead Of 1099-NEC?
As of 2020, the 1099-NEC form is used for all independent contractor income. The 1099-MISC is still a valid form. However, it is reserved for payments that are not contractor or freelancer wages, such as rent, prizes, and awards.
Do Accountants Get A 1099-MISC Or 1099-NEC?
Accountants who work as independent contractors typically receive a 1099-NEC form
What Is A 1099-NEC Used For?
The IRS has a form called 1099-NEC to report non-employee compensation. It is used to report earnings from jobs where the person is working as an independent contractor, such as freelance work or driving for companies like Uber, Lyft, or DoorDash.
What Is A 1099-MISC Form Used For?
Form 1099-MISC reports certain miscellaneous compensation, including rent, royalties, prizes and awards, healthcare payments, and payments to an attorney.
See more related articles:
Difference Between 1099 and W2: What Should Employers Know?
1099 vs. 1040: Key Differences Every Taxpayer Should Know
1098 vs 1099: Which Form Should You Receive and Why?
5 Key Differences Between 1099 and LLC
Ms. Tracy has worked in human resource consulting for over 15 years. A driven entrepreneur focused on business expansion and people development. She previously worked as Country Manager for an international Australia firm that specializes in global workforce management, as well as several key roles as Business Growth Director and Executive Search Director for both large local firms to effectively drive their business growth. A strong emphasis is placed on aligning organizational priorities/objectives with business needs. She has a large network of local business leaders and a thorough understanding of the local market.









