Key Takeaways
- A pay stub is an unofficial document detailing earnings and tax obligations for an Employer of Record (EOR) W2 employee This stub verifies income, provides tax information, and helps understand compensation breakdown.
- Accurate information, outdated tax data, and neglect to save pay stub records are common mistakes with this stub.
What Is A Pay Stub?
A pay stub meaning, also called a paycheck stub or pay slip, is a document that provides employees with a breakdown of their gross earnings, deductions, and net pay.
This stub is mainly used for EOR W2 employees (W2 job roles staffing through an EOR employee service) and is issued alongside paychecks for each payment period.
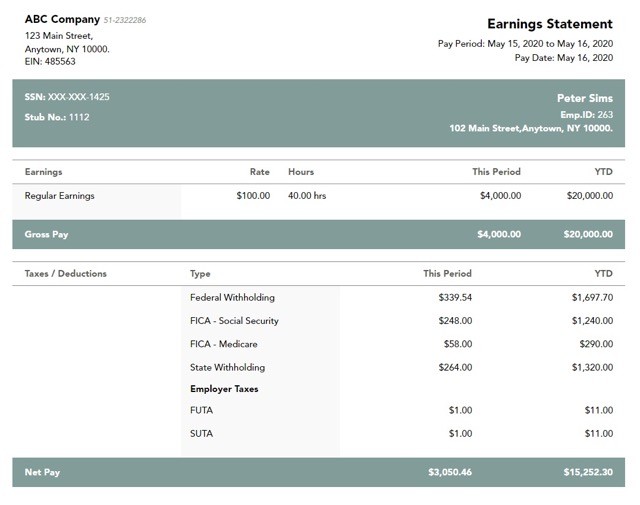
A pay stub outlines financial details related to the contractor’s earnings and tax obligations, including:
- Personal details like the employee’s name, address, and Social Security number (SSN)
- Information about the client or entity
- The number of hours worked or the scope of services provided
- Gross earnings before any deductions
- Details of federal, state, and local tax withholdings, if applicable
- Net pay, which represents the amount the contractor receives after deductions
Pay stubs are proof of income and facilitate tax reporting and compliance. Therefore, EOR W2 employees must retain copies of their pay stubs for records and tax filing purposes.
Missions of Pay Stubs
Once you understand “What is a pay stub?,” another question arises: “Why are they important?”
- Income Verification: Pay stubs prove an employee’s income over a specific period. This is crucial for determining borrowing capabilities, filing taxes, applying for mortgages, or demonstrating financial status in various situations.
- Tax Information: Pay stubs provide details about the taxes deducted from an employee’s wages, including income tax, Social Security tax, and other deductions.
- Understanding Of Compensation: Pay stubs display the components of an employee’s earnings, such as base salary, allowances, bonuses, and other deductions. They help employees understand how to calculate their wages.
What Is Included In A Paystub?
1. Personal Details
This section includes:
- Employee’s full name
- Residential address
- State of residence
- ZIP code
- Name of the hiring company, if applicable
- Time period for services rendered
- Total hours performed
- Total amount of invoice
- Bank information to receive payment
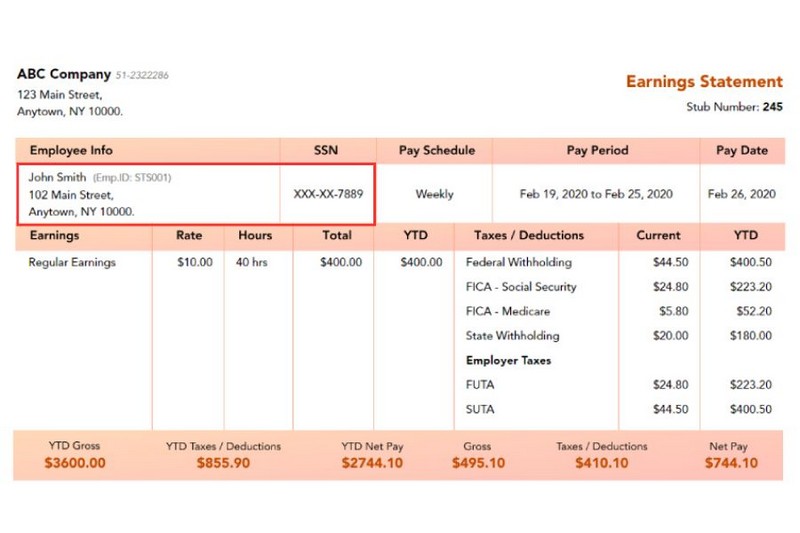
EOR W2 employees must also provide their Social Security Number (SSN) and, if applicable, contractor ID. The Internal Revenue Service (IRS) assigns this unique nine-digit number for business identification and tax purposes.
2. Salary Details
This section includes the recurring timeframe in which you earn money for your services, referred to as the Pay Period.
EOR W2 employees typically establish their pay periods as weekly, bi-weekly, semi-monthly, or monthly. It depends on the scope of their work and the labor regulations of their state. For example, your pay period might run weekly from 19/02/2020 to 25/02/2020 like this:
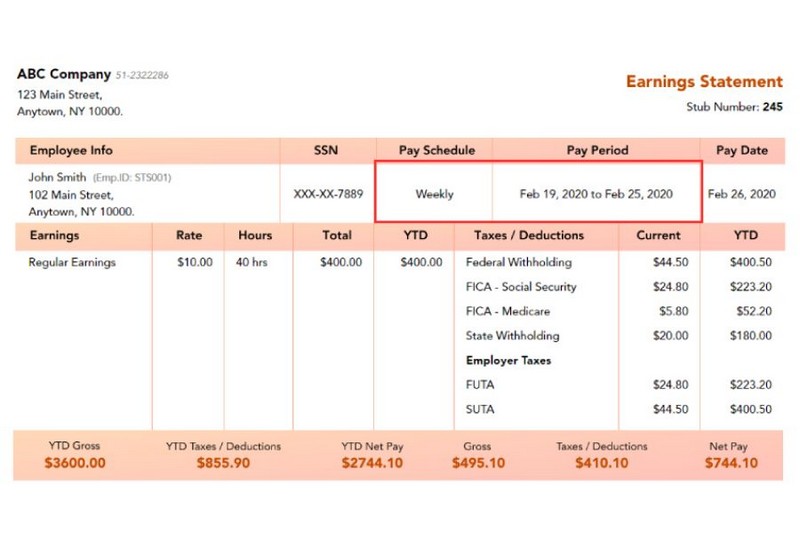
The Pay Date in the next column indicates when you expect clients to compensate you for your services.
The section below requires you to specify whether you work hourly or on a salary. If you receive hourly compensation, include your rate and the total hours worked during the selected pay period. Do a quick math calculation to calculate total and Year-to-date (YTD) earnings.
Note: When filling out your pay stub, ensure that your chosen payment structure aligns with your work type and complies with state labor laws.
3. Taxes and Deductions
This section outlines your tax and deduction information, including:
- Income tax amount
- Social Security and Medicare taxes
- Other deductions include health insurance, social security contributions, and 401(k) contributions (if applicable).
- Employer taxes
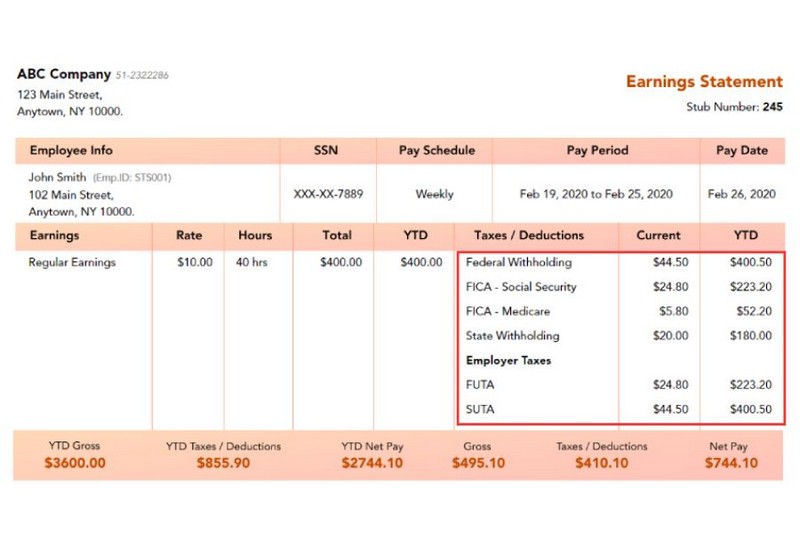
After inputting your earnings and deductions, the form, generated by your EOR payroll software, will automatically calculate your net pay. This number reflects the amount you receive after all taxable deductions are accounted for.
Common Mistakes That Can Appear On A Pay Stub
1. Providing Inaccurate Information
Inaccuracy and incompleteness in the information provided on pay stubs can confuse or even get you in trouble with the law. They sometimes lead to complications during tax filing, requiring you to reevaluate income and expenses when completing forms.
Errors often stem from improper deduction calculations or overlooking pay period dates.
Therefore, you should take the necessary care and recheck to ensure that the information on your pay stubs is accurate and complete.
2. Neglecting Pay Stub Records
After generating pay stubs, many employees frequently overlook the importance of storing them carefully for future reference. As a result, applying for loans or securing property rentals can be challenging without pay stubs as income evidence.
To solve this problem, we recommend saving electronic pay stubs to personal computers, cloud storage platforms, or external hard drives for easy access.
Ms. Tracy has worked in human resource consulting for over 15 years. A driven entrepreneur focused on business expansion and people development. She previously worked as Country Manager for an international Australia firm that specializes in global workforce management, as well as several key roles as Business Growth Director and Executive Search Director for both large local firms to effectively drive their business growth. A strong emphasis is placed on aligning organizational priorities/objectives with business needs. She has a large network of local business leaders and a thorough understanding of the local market.









